

Stata tip 2: Building with floors and ceilings.
#Stata xline color how to
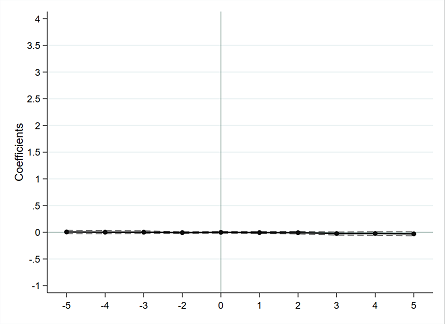
There is a choice in there of 500 as a suitable step size subject-matter knowledge will often make that choice easy, or ambitious readers may wish to think how to automate a choice.Ĭox, N. See Cox (2003) for more on building with floors and ceilings. Conversely, the call to floor() rounds to the nearest multiple of 500, but always to the same value or downwards. Weight | 74 3019.459 777.1936 1760 4840The call to ceil() (think 'ceiling' if the function is new to you) rounds to the nearest multiple of 500, but always to the same value or upwards. Estimation commands store their results in the so-called e () returns (type ereturn list after running an estimation. Options yline(linearg), xline(linearg), and tline(time linearg) specify the y, x, and t (time) values where lines should be added. regression models) and then apply coefplot to these estimation sets to draw a plot displaying the point estimates and their confidence intervals. While this book is printed in color, this does not mean that it ignores how to create monochrome (black & white) graphs.
Predicted values from this regression can then be plotted. The basic procedure is to compute one or more sets of estimates (e.g. In the nextĮxample, we regress alcuse on age interacted with id. We can also plot fitted lines using the xtline command. xtline alcuse if id < 10, overlay t(age) i(id) legend(off) scheme(s2mono) Hardin (1995) used these ideas in a Stata context and they underlie Stata's default choices. Heckbert (1990) gave an excellent first stab at simple rules.
'Nice' is easy to recognise-2 and 50 are nice but 1.9786 and 49.435 are not-but harder to define. Try separate xlines, like this: tw (scatter price mpg) (lfit price mpg, xline (20) xline (30, lpattern (dash)) DVN On Fri, at 11:39 AM, Ivica RubilTo do this, we add overlay to our command. Then consider that we usually want 'nice' rounded numbers to be shown. Suppose we are interested in seeing all of the above lines in one plot. This example generates plots for the first 9 children’s observations in the file xtline alcuse if id < 10, t(age) i(id) scheme(s2mono) A separate plot will be created for eachĭifferent id value. The time variable we specify willĪppear on the horizontal axis.
 graph
graph 
The outcome that we wish to examine,Īlcohol use, will appear on the vertical axis. Disclaimer: we are not affiliated with Stata. Syntax 2 is used to display an overview of multiple palettes in a single graph, without returning the colors in r(). We indicate that our time variable is age with t(age) and our Stata 15, an opacity level specied as 'color int op ' ,whereint 2 0,1) makes the color lighter, int > 1 makes the color darker, and op is a number between 0 (fully transparent) and 100 (fully opaque). This first example shows a line connecting the three time points broken downīy id (one plot per child). Produces plots in grayscale, because publications often require monochromatic plots.įirst, we read in the data file. Of alcohol use, alcuse, taken at ages 14, 15 and 16 for 82 children We will show a number of examples from a data file which contains a measurement The xtline command allows you to generate linear plots for panel data.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
